

Single Depth Image Super-Resolution Using Convolutional Neural Networks
A Fast Deconvolution-Based Approach for Single Image Super-resolution with GPU Acceleration
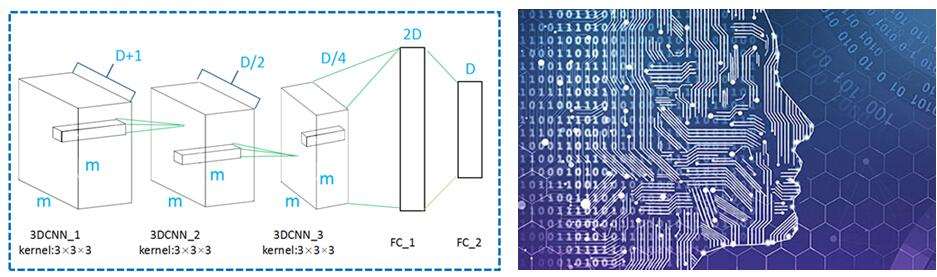
Deep Feature Embedding Learning for Person Re-Identification Using Lifted Structured Loss
Automatic Segmentation and Cardiopathy Classification in Cardiac MRI Images Based on Fully Convolutional Neural Networks
TV-SVM: Support Vector Machine with Total Variational Regularization
Perceptual stereoscopic video coding using depth-of-focus blur effects
Example-based video stereolization (EBVS) for 2D-to-3D conversion
Joint geodesic depth propagation and depth up-sampling
Visual comfort assessment and enhancement based on saliency and DIBR
Reliability-based discontinuity-preserving stereo matching

Semantic annotation based on semi-supervised learning and constraint propagation
Kernel sparse representation-based classification using multi-objective optimization
Content-based summarization and retrieval for news and sports videos
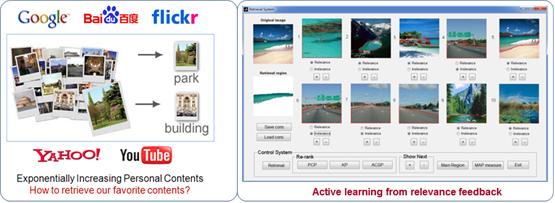
Interactive image retrieval by active learning from relevance feedback
Videotext detection, segmentation, and recognition
Novel Bayesian deringing method using spatial-gradient-local-inhomogeniety prior
Face super-resolution based on convex optimization (l1-norm)
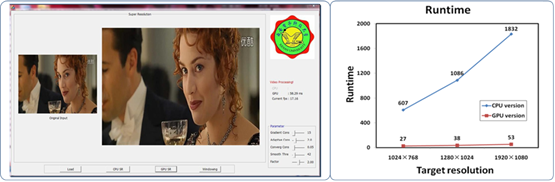
Parallelization of super-resolution reconstruction on GPU and multi-core platforms
Curvature-preserving super-resolution with gradient-consistency-anisotropic-regularization prior
Dictionary-based super-resolution with nonlocal total variation regularization
High dynamic range imaging by tone mapping and multi-exposure fusion
Specularity removal in color images
Interactive image segmentation by user interactions such as makers and touch
Power-constrained contrast enhancement for low power LCD displays

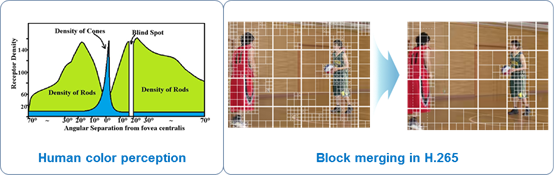
Perceptual image/video coding using human color perception
Perceptual rate distortion optimization using free energy principles and structural similarity
Blocking artifact reduction using sparse representation
Perceptual block merging for quad-tree based partitioning in H.265
Motion compensated prediction and interpolation in H.265
Xidian Media Lab has been supported by:
(1) Organization Department of the CPC Central Committee
(2) National Natural Science Foundation of China
(3) Ministry of Science and Technology
(4) China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
(5) Novatek Electronics
(6) Samsung SDS
(7) Huawei Technologies
(8) ZTE Corporation
(9) Institute of Information and Communication Technology Promotion (IITP)
We would like to acknowledge their financial support for our research.




